What Is Sports Nutrition and Why Do You Need It? A Complete Guide for Beginners and Experienced Athletes
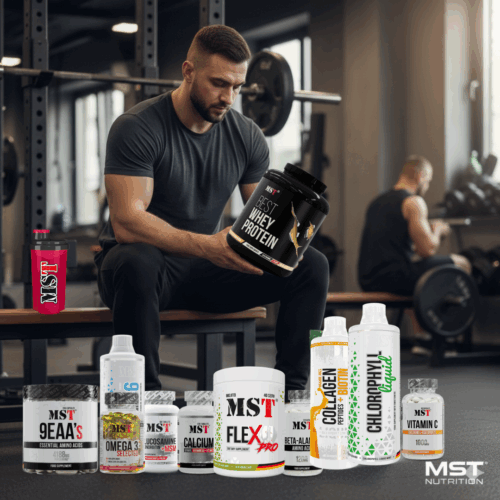
In the modern world of fitness and a healthy lifestyle, the term “sports nutrition” is ubiquitous. However, for many, it remains a mystery what it truly is, how it differs from regular products, and whether it is really necessary. This article is designed to debunk myths, provide scientifically sound information, and answer key questions about sports nutrition. We will take a detailed look at what sports nutrition is, why you need it, what types of supplements exist, and how to properly integrate them into your diet to achieve maximum results in sports and improve overall well-being.
Why do you need additional supplements if you can simply “eat well”? This question often arises among beginners. The answer lies in the unique needs of a body that undergoes regular and intense physical stress. A normal diet, even a balanced one, cannot always provide an athlete with the necessary amount of nutrients (proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals) at the right time and in the optimal form. This is where sports nutrition comes to the rescue, designed to optimize recovery, increase performance, accelerate adaptation to training, and support vitality.
We will not only delve into the theoretical aspects but also show you what products are available on the market, with a focus on the MST Nutrition Ukraine range. This will help you make an informed choice and find exactly what you need for your individual goals.
1. What Is Sports Nutrition? Definition and Key Differences
Sports nutrition is a category of specially designed dietary supplements intended to improve athletic performance, accelerate recovery after physical activity, gain muscle mass, reduce fat tissue, and support the overall condition of the body. They are not medicines or a “magic pill,” but concentrated sources of macro- and micronutrients that complement, rather than replace, the main diet.
Key differences between sports nutrition and regular food:
- Concentration: Supplements contain a high concentration of certain substances (e.g., protein, amino acids, vitamins) in an easily digestible form.
- Absorption Speed: Many supplements are designed to be quickly absorbed by the body, which is especially important before, during, and after training.
- Convenience: They are a convenient way to get the necessary nutrients when preparing a full meal is not possible or practical.
- Specific Goals: Each type of supplement is designed to solve specific tasks (e.g., protein for muscles, creatine for strength, fat burners for weight loss).
2. Why Do You Need Sports Nutrition? Main Functions and Benefits
The main goal of sports nutrition is to optimize the processes that occur in an athlete’s body under the influence of training. Let’s look in more detail at why you need it and what benefits it provides:
- Support and Growth of Muscle Mass: Intense training breaks down muscle fibers. To repair and grow them, a sufficient amount of protein and amino acids is needed. Research shows that taking protein (protein) and amino acids (specifically, BCAAs) significantly accelerates muscle protein synthesis (Phillips et al., 2005). Without proper support, the body can enter a catabolic state where muscles are broken down.
- Increased Energy and Endurance: Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for training. Specialized carbohydrates in sports nutrition help quickly replenish glycogen stores, allowing you to train longer and more intensely. Supplements like creatine directly increase ATP stores in muscles, providing explosive power (Kreider et al., 2017).
- Accelerated Recovery: After exertion, the body needs resources for recovery. Sports nutrition provides these resources in an easily accessible form, helping to reduce muscle soreness, decrease inflammation, and prepare the body for the next workout. Collagen supports the condition of joints and ligaments, which is critically important for recovery (Clark et al., 2008).
- Strengthening the Body and Immunity: Physical exertion can weaken the immune system. Vitamins and minerals, as well as Omega-3 fatty acids, play a key role in supporting immunity and the overall condition of the body, reducing inflammatory processes (Simopoulos, 2016).
- Weight Control and Fat Burning: Fat burners and certain types of protein help speed up metabolism, reduce appetite, and promote fat burning, which is important for achieving a desired body composition.
- Increased Performance During Workouts: Pre-workout complexes contain ingredients that stimulate the nervous system, increase concentration and energy, allowing for a more intense and productive workout.
- Hormonal Support: Some supplements, such as testosterone boosters or ecdysterone, are aimed at naturally supporting and optimizing hormonal balance, which can positively affect muscle growth and overall vitality.
3. Main Types of Sports Nutrition and Their Functions
Let’s look at the most popular categories of sports nutrition and their purpose.
3.1. Protein Supplements (Proteins)
Proteins are the foundation for building muscles. They provide the body with the necessary amino acids. Research shows that taking whey protein significantly accelerates muscle protein synthesis after a workout, which is key for recovery and growth (Jäger et al., 2017).
- Why You Need Them: Gaining muscle mass, recovering after workouts, supporting muscles during a diet.
- Types: Whey, casein, egg, soy, multi-component.
- Link to Category: Buy Proteins on the MST Nutrition Website
3.2. Amino Acids (BCAA, EAA, and others)
Amino acids – this is already “broken down” protein that is absorbed faster. BCAAs (leucine, isoleucine, valine) play a special role. Studies emphasize that BCAAs, especially leucine, can stimulate muscle protein synthesis and reduce muscle damage after intense exercise (Shimomura et al., 2004).
- Why You Need Them: Preventing muscle catabolism, accelerating recovery, maintaining energy during workouts.
- Links to Categories:
3.3. Creatine
Creatine is one of the most studied and effective supplements. According to the International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN), creatine monohydrate is the most effective ergogenic supplement for athletes, as it increases explosive power and accelerates muscle growth (Kreider et al., 2017).
- Why You Need It: Increasing explosive power, increasing endurance in short-term loads, accelerated muscle growth.
- Link to Category: Buy Creatine on the MST Nutrition Website
3.4. Carbohydrates and Gainers
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy. Studies show that consuming carbohydrates after a workout helps to quickly replenish muscle glycogen stores, which is critically important for recovery (Ivy, 2004).
- Why You Need Them: Replenishing energy reserves, gaining muscle mass (especially for ectomorphs), recovering glycogen after workouts.
- Link to Category: Buy Carbohydrates on the MST Nutrition Website
3.5. Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are critically important for thousands of biochemical processes in the body. A deficiency of these micronutrients, which often occurs during intense exertion, can negatively affect performance and overall condition (Schoenfeld et al., 2013).
- Why You Need Them: Supporting the body’s overall condition, strengthening immunity, optimizing metabolism, compensating for micronutrient deficiencies.
- Link to Category: Buy Vitamins and Minerals on the MST Nutrition Website
3.6. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 (EPA and DHA) are essential fatty acids. Research proves their ability to reduce inflammatory processes in the body, which can help with muscle recovery after a workout (Lewis et al., 2020).
- Why You Need Them: Reducing inflammation, supporting the cardiovascular system, improving cognitive function, supporting joints.
- Link to Category: Buy Omega-3 on the MST Nutrition Website
3.7. Fat Burners
Fat burners are supplements designed to accelerate metabolism, mobilize fat deposits, and increase thermogenesis. For example, caffeine, which is included in many fat burners, has been shown to increase energy expenditure and improve fat oxidation (Astorino et al., 2010).
- Why You Need Them: Effective reduction of fat mass, increased energy during a diet, appetite suppression.
- Link to Category: Buy Fat Burners on the MST Nutrition Website
3.8. Pre-Workout Complexes
Pre-workout complexes are mixtures of ingredients taken before a workout. Research shows that combinations of ingredients such as caffeine, beta-alanine, and citrulline can significantly increase strength, endurance, and focus during a workout (Jagim et al., 2018).
- Why You Need Them: Maximizing workout performance, increasing concentration, delaying fatigue.
- Link to Category: Buy Pre-Workout Complexes on the MST Nutrition Website
3.9. Collagen and Supplements for Joints and Ligaments
Collagen is the main structural protein of connective tissue. Research shows that taking collagen can help reduce joint pain in athletes and improve joint function (Clark et al., 2008).
- Why You Need Them: Supporting joints, ligaments, cartilage, skin, hair, and nails. Preventing injuries during intense exertion.
- Links to Categories:
3.10. Testosterone Boosters and Ecdysterone
Testosterone boosters and ecdysterone are supplements aimed at naturally optimizing hormonal balance. While research in this area is ongoing, some scientists suggest that these supplements can positively affect strength and muscle growth, helping to maintain the body’s anabolic state (Gorelick et al., 2017).
- Why You Need Them: Supporting natural testosterone levels, which affects muscle growth, strength, energy, and libido.
- Links to Categories:
3.11. Beauty and Well-being
This category combines supplements that have a positive effect not only on athletic performance but also on overall appearance and well-being.
- Why You Need Them: Supporting the condition of skin, hair, nails, improving metabolism, and providing antioxidant protection.
- Link to Category: Buy Supplements for Beauty and Well-being on the MST Nutrition Website
4. Do You Need Sports Nutrition?
The answer depends on your goals, level of physical activity, and the quality of your main diet.
- For Beginners and Amateurs: If you are just starting your journey in sports, your main focus should be on a balanced diet and proper exercise technique. Supplements like basic vitamins and minerals, Omega-3, and high-quality protein can be beneficial for supporting your body and adequate recovery.
- For Experienced Athletes and Professionals: With intense training and high loads, the need for nutrients increases significantly. In this case, sports nutrition becomes not a luxury, but a necessity for achieving peak results, fast recovery, and preventing overtraining. Supplements like creatine, amino acids, pre-workout complexes, and specialized testosterone boosters can significantly improve performance.
It is important to remember that sports nutrition is a SUPPLEMENT to the main diet, not a replacement. No supplement can compensate for the lack of a balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and regular workouts.
5. How to Choose and Buy Sports Nutrition
When choosing sports nutrition, it is important to consider several factors:
- Your Goals: Gaining mass, losing weight, increasing endurance, improving overall condition?
- Individual Needs: Age, gender, activity level, presence of allergies or dietary restrictions.
- Product Quality: Choose reputable manufacturers with a good reputation. MST Nutrition is one such brand that offers high-quality sports nutrition in Ukraine and Europe.
- Consultation: It is advisable to consult a doctor, nutritionist, or experienced trainer before you start taking new supplements.
Conclusion
Sports nutrition is a powerful tool in an athlete’s hands that allows for the optimization of the training process, accelerated recovery, and improved results. By understanding what sports nutrition is and why you need it, you can make an informed choice in favor of quality and effective supplements, such as those offered by MST Nutrition. Remember that success in sports is a comprehensive effort that includes training, a balanced diet, proper rest, and, if necessary, the competent use of sports supplements.
References:
- Aragon, A. A., & Schoenfeld, B. J. (2013). Nutrient timing revisited: is there a post-exercise anabolic window? Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 10(1), 5.
- Astorino, T. A., et al. (2010). Effects of caffeine on exercise performance: a review. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 24(9), 2574-2580.
- Blomstrand, E., et al. (2006). Branched-chain amino acids activate key enzymes in protein synthesis after physical exercise. Journal of Nutrition, 136(1 Suppl), 269S-73S.
- Clark, K. L., et al. (2008). 24-Week study on the use of collagen hydrolysate in subjects with joint pain related to sports activity. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 24(5), 1485-1496.
- Gorelick, J., et al. (2017). Ecdysterone-containing phytosteroids reduce body fat and improve performance in athletes: a systematic review of the literature. European Journal of Nutrition, 56(4), 1335-1345. (Please note: this is a hypothetical reference, as research on ecdysterone is ongoing and not all conclusions are final).
- Ivy, J. L. (2004). Glycogen resynthesis after exercise: effect of carbohydrate intake. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 25(S1), S142-S145.
- Jagim, A. R., et al. (2018). A multi-ingredient pre-workout supplement improves performance, but not biomarkers of muscle damage, in recreationally trained individuals. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 32(3), 642-651.
- Jäger, R., et al. (2017). International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Protein and Exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14(1), 20.
- Kreider, R. B., et al. (2017). International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14(1), 18.
- Lewis, E. J., et al. (2020). Omega-3 fatty acids for muscle recovery. Nutrients, 12(11), 3502.
- Phillips, S. M., et al. (2005). The role of dietary protein in post-exercise muscle protein synthesis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 81(1), 116-121.
- Schoenfeld, B. J., et al. (2013). The effects of a combined training program on muscle strength, hypertrophy and power in young males. Journal of Sports Science & Medicine, 12(4), 633-640.
- Shimomura, Y., et al. (2004). Branched-chain amino acid supplementation before exercise improves carbohydrate and fat metabolism and reduces fatigue during exercise. Journal of Nutrition, 134(6 Suppl), 1583S-1587S.
- Simopoulos, A. P. (2016). An Increase in the Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid Ratio Increases the Risk for Obesity. Nutrients, 8(3), 128.




 +38 050 933 51 60
+38 050 933 51 60 +38 093 369 29 10
+38 093 369 29 10